Siliconit Heating Elements, SiC Refractory and Insulating Materials
[ SILICONIT Co., Ltd. ]
Product Overview
Siliconit Heating Elements are Silicon Carbide (SiC) Heating Elements.
Their primary application is integration as heaters within electric furnaces, effectively supporting a wide temperature range, typically from 800℃ to 1600℃.
These elements are widely utilized in numerous industrial and academic research fields, including: General Industry, Automotive, Electrical and Semiconductor, Medical, Glass (Optical), Steel, Non-ferrous Metals, Recycling, Advanced Science and Research.
We also provide coated heating elements specifically designed for stable operation under special atmospheric conditions (e.g., reducing or corrosive environments).
Porandom Refractories are manufactured from porous alumina.
Their low heat capacity significantly contributes to energy savings and improved furnace efficiency.
Silicondam Refractories are characterized by excellent thermal conductivity and superior resistance to thermal shock (rapid heating and cooling).
Heating Element Types

Rod-Type Siliconit
Rod-Type Siliconit (Silicon Carbide Heating Elements)
This is our most standard type of heating element, manufactured using our proprietary and unique process.
We offer a wide range of standard sizes, and dimensions other than standard specifications can also be custom-made (or customized) to meet specific requirements.

Spiral-Type Siliconit.
Spiral-Type Siliconit (Silicon Carbide Heating Elements)
These elements feature a spiral groove (or helical groove) cut into the tube surface.
They are typically capable of operating at higher temperatures than the Rod-Type Siliconit.
Larger diameter models can accommodate the heated material inside the tube, allowing them to be utilized as a tube furnace.
The terminals are connected using metal bands.

Double-Leg Siliconit (or U-Type Siliconit)
Double-Leg / U-Type Siliconit (Silicon Carbide Heating Elements)
This heating element is a variation of the Spiral-Type Siliconit, featuring a modified groove design that allows the terminals/electrodes to be concentrated on one end.
This enables greater flexibility in furnace design.
Larger diameter models can accommodate the heated material inside the tube, allowing them to be utilized as a tube furnace.
The terminals are connected using metal bands.

Spiral-Type Siliconit (SS Type) (Silicon Carbide Heating Elements)
This heating element features a spiral groove cut into its rod-shaped body, enabling operation at higher temperatures compared to the Rod-Type elements.
Important Note: Due to the spiral configuration, these elements are more susceptible to mechanical damage than the standard Rod-Type elements and must be handled with care.
Spiral R-Type Siliconit (SSR Type) (Silicon Carbide Heating Elements)
This heating element is characterized by a spiral groove cut into a rod-shaped body, featuring both terminals concentrated on one end.
This design allows for higher operating temperatures than standard Rod-Type elements.
The concentration of the electrodes on a single furnace wall simplifies maintenance and inspection.
This type of element is highly recommended for use in high-temperature ranges, as the service life of Rod-Type heating elements is significantly shortened under such conditions.
Important Note: These elements are more susceptible to mechanical damage compared to the standard Rod-Type elements and must be handled with care.

Hairpin-Type Siliconit (HPL Type)
This heating element features a unique design with both terminals concentrated on one end, allowing the electrodes to be situated on a single side.
This configuration significantly simplifies element replacement.
The HPL type is ideal for applications where the furnace structure imposes design restrictions and can be utilized across the same temperature range as the Rod-Type elements.
While the joints do not generate heat in the same manner as the heating section, they are designed to withstand the same high temperatures and can therefore be used exposed inside the furnace.
The Siliconit Heating Elements described above are available in a wide variety of standard sizes.
Furthermore, we are equipped to handle custom orders for special sizes and resistance values outside of our standard specifications.
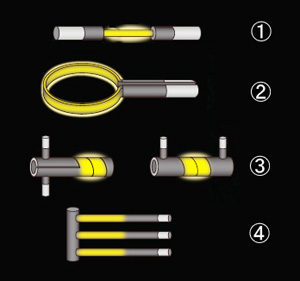
Specialty Siliconit Heating Elements (Custom Shapes)
We also manufacture a variety of heating elements under our Specialty Siliconit category, including the following types:
1)Infrared Light Source Siliconit (IRH Type)
2)Ring-Type Siliconit (SR Type)
3)DSPT Type and SPT Type Siliconit
4)Three-Phase Siliconit (WHP Type)
We can also prototype and manufacture special shapes tailored to meet your specific needs. Please contact us directly to discuss your custom requirements.
Refractories for Electric Furnaces

Porandom Refractory and Insulating Materials
Porandom is a porous, lightweight alumina-based refractory and insulating material characterized by extremely high refractoriness (high melting point), very low heat capacity, and excellent heat retention.
This combination of properties allows the furnace temperature to be raised efficiently using less power, contributing significantly to energy savings.
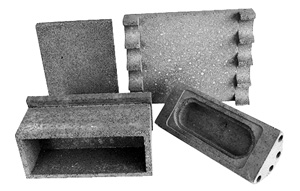
Silicorundum Refractories
Silicorundum is a material manufactured by sintering Silicon Carbide (SiC) as its raw material.
The key features of Silicorundum include:
Extremely high thermal conductivity compared to standard refractories.
Outstanding resistance to oxidation and excellent thermal shock resistance (resistance to rapid heating and cooling).
Silicorundum is ideally suited for use as shelving (setter plates) in various firing furnaces, saggars, and special furnace linings.

Recrystallized Silicon Carbide (R-SiC)
Silicolite Recrystallized Silicon Carbide Refractories (R-SiC)
Silicolite is manufactured using high-purity Silicon Carbide (SiC) as its raw material.
Because it is sintered at ultra-high temperatures without the use of bonding agents, it contains no impurities and therefore will not contaminate the furnace environment even when utilized at extremely high temperatures.
Important Usage Note: If Silicolite is used at temperatures of 1400℃ or higher in a hydrogen (H2) or nitrogen (N2) atmosphere, SiH2 or SiNx may be generated, leading to material deterioration.
Please consult with us prior to use under these specific conditions.